
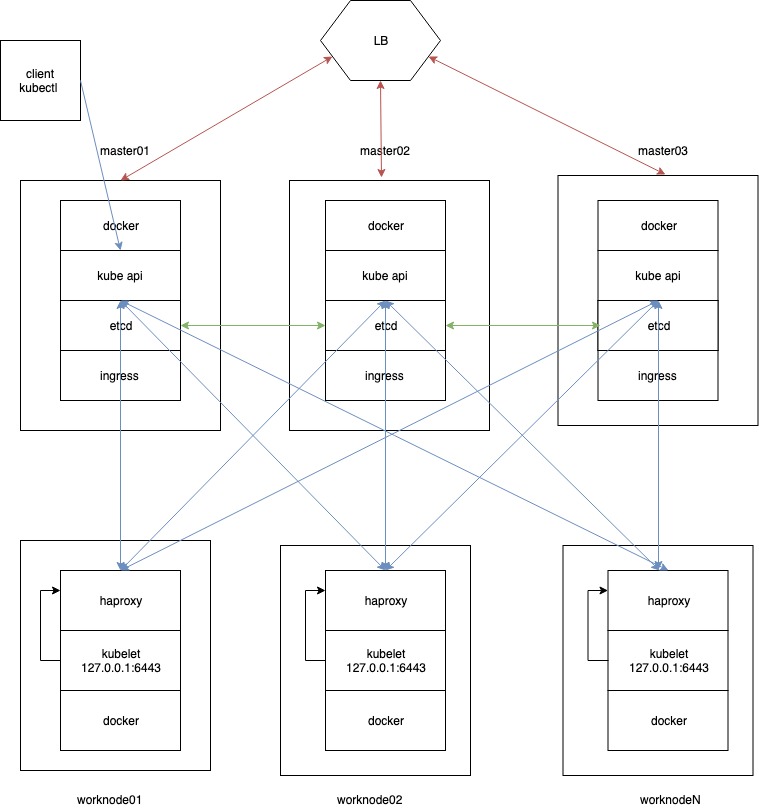
Start by disabling the swap memory on each server: sudo swapoff –a Step 7: Assign Unique Hostname for Each Server Nodeĭecide which server to set as the master node. Kubernetes Deployment Step 6: Begin Kubernetes Deployment
Install kubernetes cluster habr update#
For update instructions, please see the developers’ instructions. Also, this process prevents apt from automatically updating Kubernetes. Different versions can create instability.
Install kubernetes cluster habr install#
Note: Make sure you install the same version of each package on each machine. Verify the installation with: kubeadm version Install Kubernetes tools with the command: sudo apt-get install kubeadm kubelet kubectl sudo apt-mark hold kubeadm kubelet kubectlĢ. The tool gives you command-line access to clusters.ġ. Kubelet is the work package, which runs on every node and starts containers. It fast-tracks setup by using community-sourced best practices. Kubeadm (Kubernetes Admin) is a tool that helps initialize a cluster. To add them, enter the following: sudo apt-add-repository "deb kubernetes-xenial main" Kubernetes is not included in the default repositories. Then repeat the previous command to install the signing keys. If you get an error that curl is not installed, install it with: sudo apt-get install curlĢ. Enter the following to add a signing key: curl -s | sudo apt-key add Since you are downloading Kubernetes from a non-standard repository, it is essential to ensure that the software is authentic.

Install Kubernetes Step 3: Add Kubernetes Signing Key To start Docker if it’s not running: sudo systemctl start dockerģ. Verify Docker is running: sudo systemctl status docker Set Docker to launch at boot by entering the following: sudo systemctl enable dockerĢ. Check the installation (and version) by entering the following: docker ––version Step 2: Start and Enable Dockerġ. Repeat the process on each server that will act as a node.Ĥ. Next, install Docker with the command: sudo apt-get install docker.ioģ.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
